Trump has been President for 1 year and fighting against Biden and the Democrats economic misery.
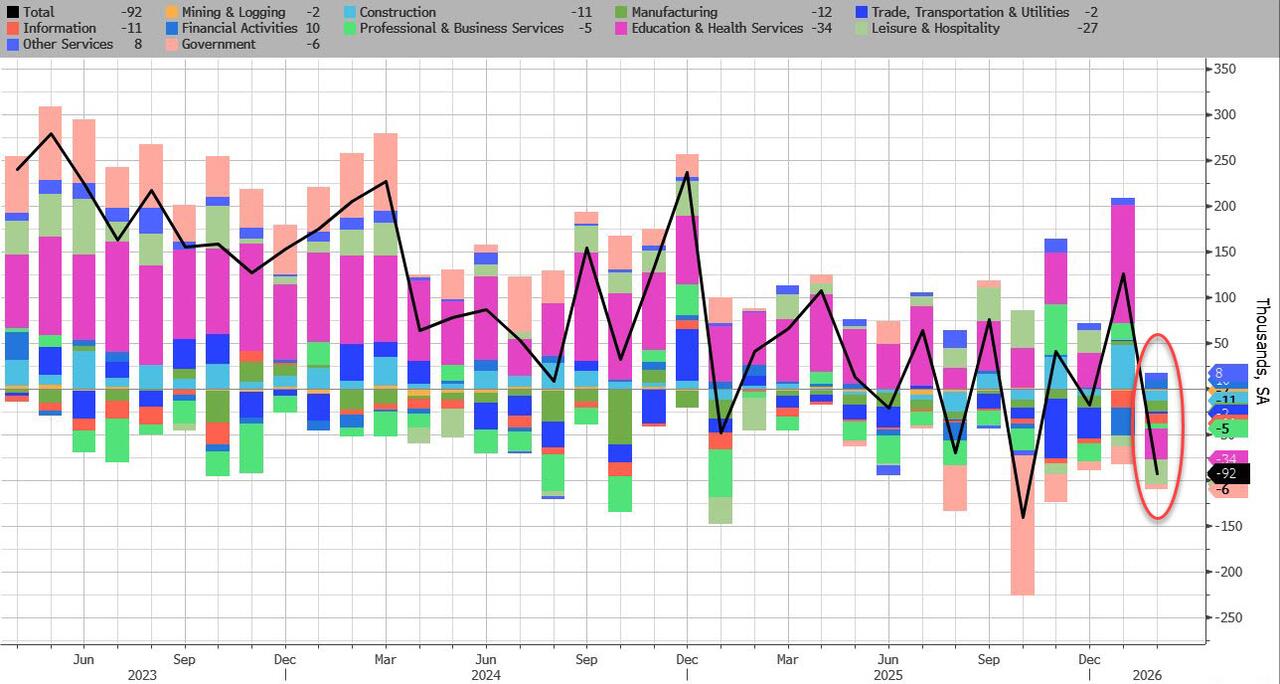
In February, the US lost 92,000 jobs, a huge drop from the downward revised 126K in January, and the second worst print since 2020 (only October’s shock -140K was worse), and this time, the massive drop can’t be dismissed as a one-time drop in government payrolls. The number of private payrolls dropped by 86K, also a huge miss to estimates of a 60K increase.

One potential mitigating factor: the number of people who were unable to work due to weather surged to 228K in February, well above last year’s level 167K, due to the powerful winter storms hitting the US.

- The number of long-term unemployed (those jobless for 27 weeks or more) changed little at 1.9 million in February but is up from 1.5 million a year earlier. The long-term unemployed accounted for 25.3 percent of all unemployed people in February.
- The number of people employed part time for economic reasons decreased by 477,000 to 4.4 million in February. These individuals would have preferred full-time employment but were working part time because their hours had been reduced or they were unable to find full-time jobs.
- The number of people not in the labor force who currently want a job changed little in February at 6.0 million. These individuals were not counted as unemployed because they were not actively looking for work during the 4 weeks preceding the survey or were unavailable to take a job.
- Among those not in the labor force who wanted a job, the number of people marginally attached to the labor force changed little at 1.6 million in February. These individuals wanted and were available for work and had looked for a job sometime in the prior 12 months but had not looked for work in the 4 weeks preceding the survey. The number of discouraged workers, a subset of the marginally attached who believed that no jobs were available for them, decreased by 109,000 in February to 366,000.
Turning to the establishment survey, which unveiled the shocking February drop, the BLS reported a broad-based decline, driven by striking employment workers:
- Employment in health care decreased in February, reflecting strike activity. Employment in information and federal government continued to trend down. Payroll employment changed little on net in 2025.
- Health care employment declined by 28,000 in February, following a large increase in January (+77,000). Offices of physicians lost 37,000 jobs in February, primarily due to strike activity. Hospitals added 12,000 jobs. Over the prior 12 months, health care had added an average of 36,000 jobs per month.
- Employment in information continued to trend down in February (-11,000). The industry had lost an average of 5,000 jobs per month over the prior 12 months.
- In February, federal government employment continued to decline (-10,000). Since reaching a peak in October 2024, federal government employment is down by 330,000, or 11.0 percent.
- Employment in social assistance continued its upward trend in February (+9,000), driven by individual and family services (+12,000).
- Transportation and warehousing employment changed little in February (-11,000). A job loss in couriers and messengers (-17,000) was partially offset by a gain in air transportation (+5,000). Employment in transportation and warehousing has declined by 157,000, or 2.4 percent, since reaching a peak in February 2025.
- Employment showed little change over the month in other major industries, including mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction; construction; manufacturing; wholesale trade; retail trade; financial activities; professional and business services; leisure and hospitality; and other services.
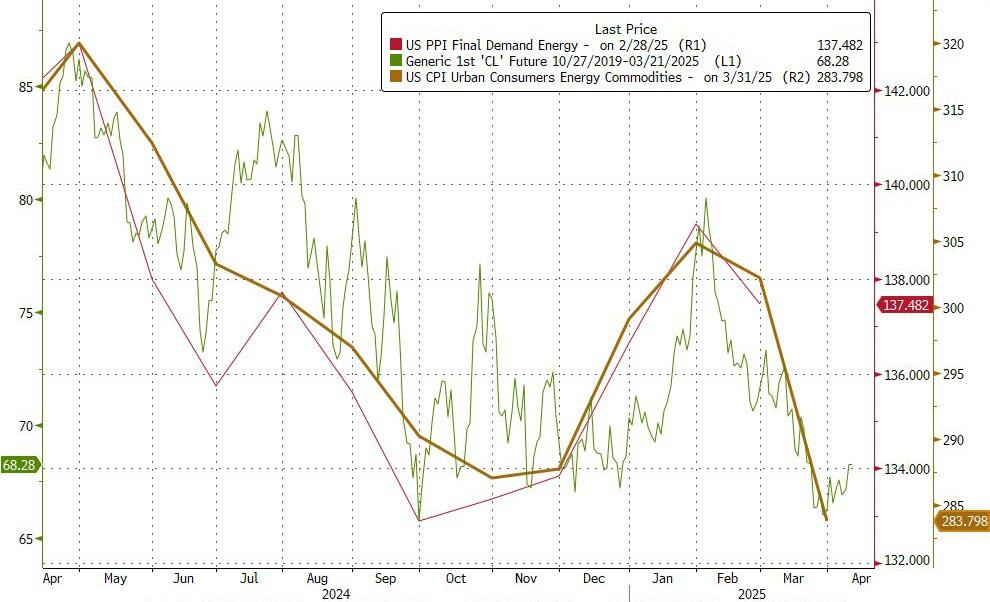
Switching to oil, we see the West Texas Intermediate and Brent Oil prices soaring on the attacks on Iran.

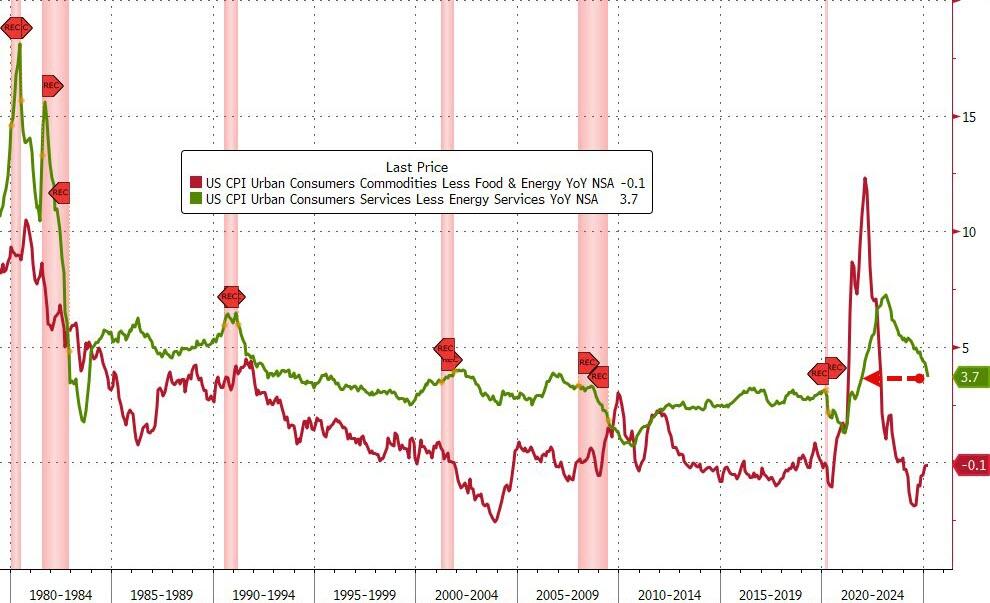
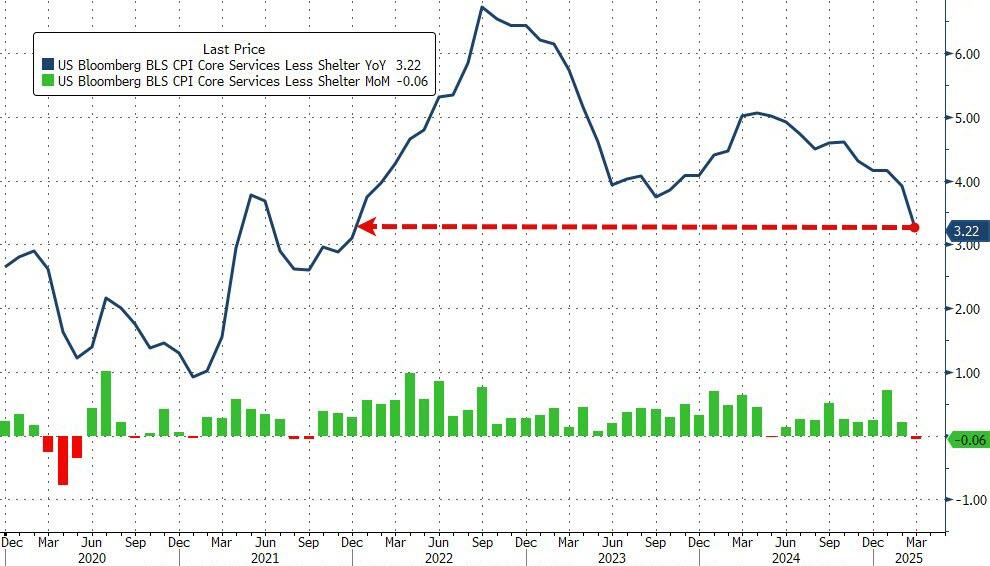
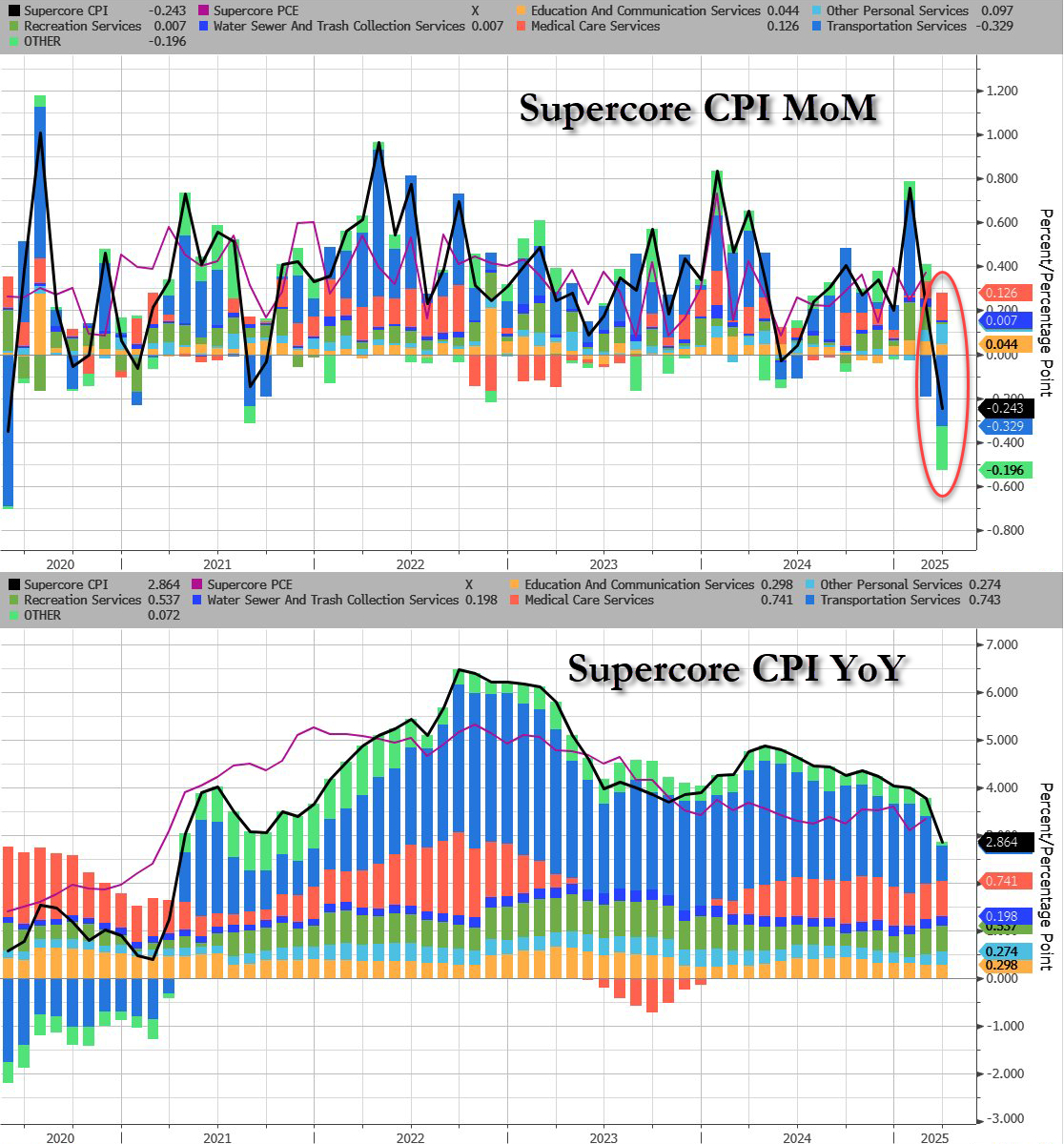
To soothe you.


























You must be logged in to post a comment.